How do the glycoproteins and glycans synthesized?
What’s the biological function of glycoproteins?
Based on techniques in biochemistry, molecular biology, cellular biology, experimental animals and computational biology, we constructed glycosyltransferase knockout cells and mice models, discovered novel glycosyltransferase inhibitors, developed glycoproteomic detection and analysis strategies using glycan metabolic labeling, lectin array and mass spectrometry analysis. Using these materials and techniques, we revealed the precise regulation mechanism and significance of protein O-glycosylation closely related to tumor and development.
Representative work:
1.ppGalNAc-T18 (GALNTL4) is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum rather than the Golgi apparatus (Glycobiology, 2012), it retains in endoplasmic reticulum depending on its luminal regions interacting with ER resident UGGT1, PLOD3 and LPCAT1 (Glycobiology, 2021), and exerts its functions in O-glycosylation and ER stress via a non-catalytic mechanism (BBA Gen Subj, 2019).
2.ppGalNAc-T13(GALNT13) contributes to neuronal differentiation through glycosylating and stabilizing PDPN (J Biol Chem, 2016).
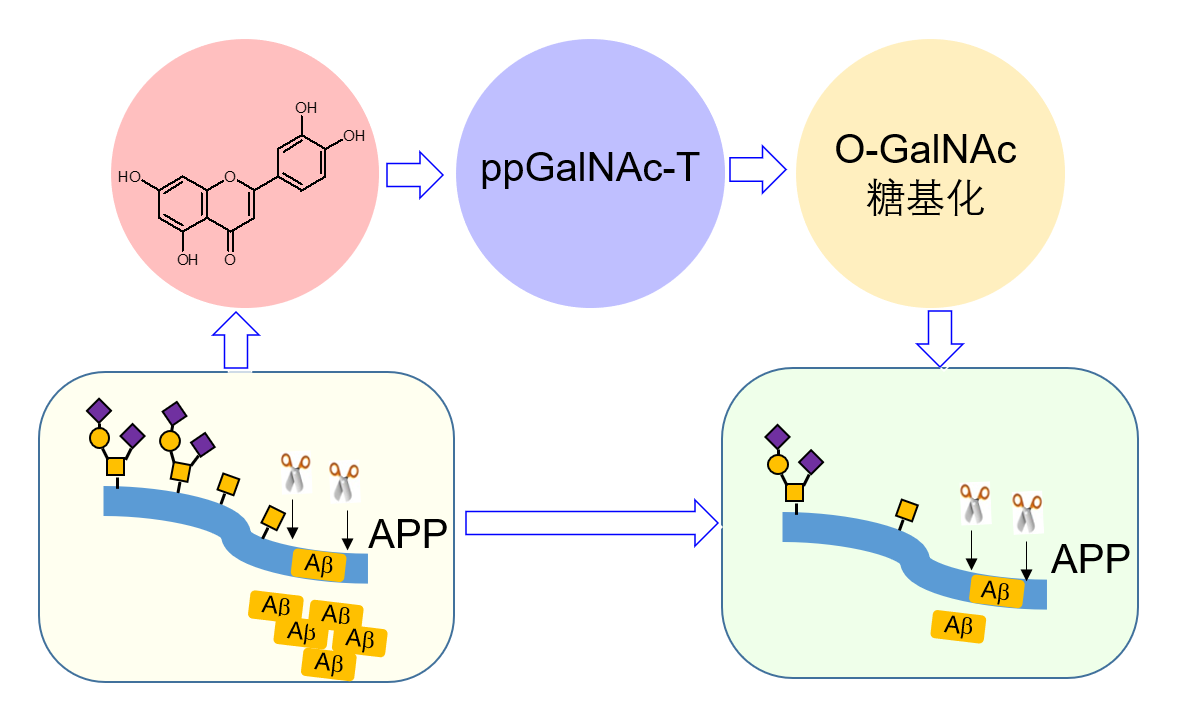
3.The small molecule luteolin inhibits ppGalNAc-Ts and reduces mucin-type O-glycosylation of amyloid precursor protein (J Biol Chem, 2017), and urolithin D (UroD) inhibits ppGalNAc-Ts activity to reduce cell O-glycosylation and lead to lowering the migration and invasion of CRC cells (Bioorg Med Chem, 2019).
4.Established an intact O-glycopeptide MS analysis strategy for APP O-glycopeptide identification with enhanced fragmentation efficiency and detection sensitivity (BBA Gen Subj, 2021).


 Back
Back